CORE HR:
} PeopleSoft’s Human Capital
Management (HCM) solution enables Human Resources (HR) (CORE HR) organizations globally to
transition from administration towards achieving workforce excellence.
PeopleSoft HCM solutions support all components of a comprehensive HCM strategy
} Core HR tells us about the key
concepts in the configuration and tables included. It deals with the
installation table and the setup related tables.
After the initial installation settings are done, the first
step in configuring the application for an organization is to Set-Up the
Organizational Master Data. This data is also referred as Foundation Data.
Types of PeopleSoft Tables
The PeopleSoft Human Resources application stores
information in various types of tables. These tables each serve different purposes. They all
function as foundation tables for storing an organization’s human resources
data.
• Translate table
• Processing and defaulting tables
• Control tables
• Transaction tables
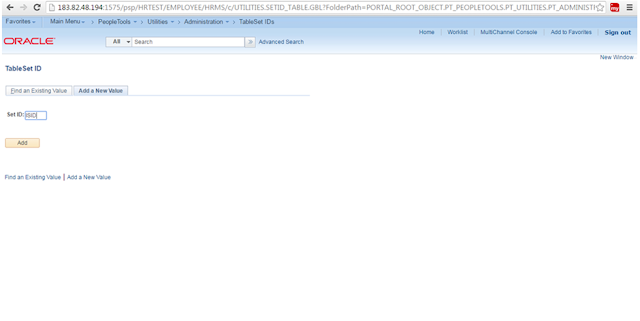
Set ID:
Set id
is a High level field in the PeopleSoft; it is an unique identification of
Control table.
To
create set ID:
With Set ID’s
definition it is possible to control what a business unit can access within a
table, as they are used to restrict or grant access to different data in a
single table thereby allowing table set sharing. In Xyz Company, each LOB (Line
of business) maintain separate department, designation etc. Set ID will be
created for each line of business so that each LOB can view respective data.
"An identification code that represents a set of control table
information or TableSets. A TableSet is a group of tables (records) necessary
to define your company’s structure and processing options." Set IDs are a
fundamental element of PeopleSoft configuration that enable flexibility and
control of control data
SetIDs - are used to group control data
• Store master data applied against transactions
• Are updated infrequently
• Define accounting structure and processing rules
• Reflect business policies, organizational structure and/or processing rules, i.e. a logical grouping relative to where the controls are to be applied
• Prime key field on control tables
• Data is usually effective dated
SetIDs - are used to group control data
• Store master data applied against transactions
• Are updated infrequently
• Define accounting structure and processing rules
• Reflect business policies, organizational structure and/or processing rules, i.e. a logical grouping relative to where the controls are to be applied
• Prime key field on control tables
• Data is usually effective dated
Navigation: People
Tools >Utilities >Administration> Table Set IDs
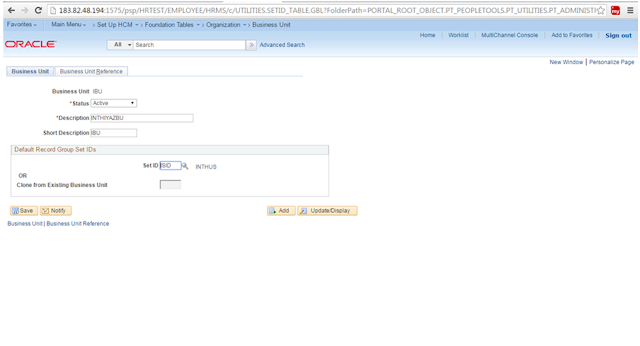
Business
Unit:
The
Business Units are logical organizational entities, determinant on many control
tables, which are a way of tracking specific business information for reporting
and for data collection. In Xyz Company, business unit will be created for each
LOB.
Store data about day-to-day business
activities
• Are updated frequently
• Define restrictions and defaults
• Control reporting and/or security
• Reflect how operations are organised, i.e. a logical grouping relative to the module function
• Prime key field on transaction tables
When a business unit is created, a setID of the same name is also created.
When a business unit is created, it is linked to a default setID (which may or may not be the one automatically created).
SetIDs can be created independent of a business unit, e.g. SHARE.
When business units are created they update records BUS_UNIT_TBL_FS and BUS_UNIT_TBL_XX (where XX represents the module) and will also update external systems (e.g. HR) if service operations (messages) for business units are active.
Data keyed by the same SetID is called a TableSet.
The combination of Business Unit and Set ID are effectively applied against a record group (a collection logically and functionally created control tables) and enable a mixing and matching of control tables with transactions (affected by those control tables). This is referred to as TableSet Control.
• Are updated frequently
• Define restrictions and defaults
• Control reporting and/or security
• Reflect how operations are organised, i.e. a logical grouping relative to the module function
• Prime key field on transaction tables
When a business unit is created, a setID of the same name is also created.
When a business unit is created, it is linked to a default setID (which may or may not be the one automatically created).
SetIDs can be created independent of a business unit, e.g. SHARE.
When business units are created they update records BUS_UNIT_TBL_FS and BUS_UNIT_TBL_XX (where XX represents the module) and will also update external systems (e.g. HR) if service operations (messages) for business units are active.
Data keyed by the same SetID is called a TableSet.
The combination of Business Unit and Set ID are effectively applied against a record group (a collection logically and functionally created control tables) and enable a mixing and matching of control tables with transactions (affected by those control tables). This is referred to as TableSet Control.
Navigation: Set Up HRMS> Foundation
Tables >Organization> Business Unit
LOCATION Setup:
The
purpose of establishing Locations in PeopleSoft application is to clearly
identify physical local place where the employees work.
PeopleSoft
Locations would be mapped with the actual Xyz Company office locations.
For each location the default holiday-schedule will also be specified.
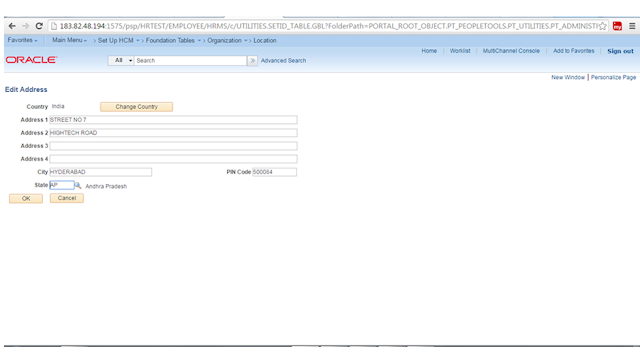
Navigation: Set
Up HRMS >Foundation Tables >Organization > Location
Location
– Location Address tab
This
page is used to record the Location description, address, phone/Fax, building,
floor, country, etc.
Location
– Location Profile tab
This
page is used to store the location profile information, such as:
§ Salary Default – The Set id and Salary plan
will be used to default the salary information
§ Regulatory Region or Region
§ Holiday Schedule – a code defined with the
specific holidays of the Location
§ Division – linked with the location
Each
Line of Business shares the Locations and thus, one set id will be created for
each Line of Business. If a location is common for State and Corporate Office
or State and Unit Office a different location code will be configured to enable
accurate data security. The list of locations will be finalized in Steering.
Sub-Location: The purpose of establishing Sub
Locations in PeopleSoft application is to clearly identify physical local place
where the employees work.
PeopleSoft Sub Locations would be mapped with the actual Xyz Company
PeopleSoft Sub Locations would be mapped with the actual Xyz Company
Company Setup:
The
purpose of the Company table is to define organization’s legal business
entities.
Navigation: Set Up HRMS>
Foundation Tables >Organization >Company
Company– Location tab
Company is defined with code, the effective
date from which it exists, short and long description of the company and the
address. It can be associated with the Location, if it was already set up, and
the corresponding set ID.
PeopleSoft allows 3 characters for Company
code. Also, the EFFDT can be set for all companies as ’01-01-1900’ to avoid any
data discrepancies.
Company– Default Settings tab
This page is used to specify default company
information, like regulatory region and currency code. The values can be
overridden at job level. Payroll for North America will be ignored, as well as
the linked fields.
Company– Phones tab:
This page can be used to define the company’s industry (type of industry and industry sector) and the phone numbers of the company, like business, fax, etc.
This page can be used to define the company’s industry (type of industry and industry sector) and the phone numbers of the company, like business, fax, etc.
Company– Rules Definition tab:
This page can be used
to define the decimal precision for Full-Time Equivalency, so the purpose is to
enter the number of decimal positions that the system will use to calculate
FTE. FTE is used for calculating the employees pay on basis of hours worked.
This feature will not be required for DB.
Department Setup:
The Departments are an important definition of the
organizational structure. Based on the Department, the Location code, company
and manager ID can be defaulted at the worker level. Xyz Company has currently
many Departments/Verticals such as Finance and Accounts, HR, Editorial etc.
These departments can be mapped to PeopleSoft departments. These departments
typically have parent level department or verticals. Each vertical will have
respective corporate head, state heads and unit heads.
Navigation: Set
Up HRMS> Foundation Tables> Organization> Departments
Departments – Profile
In this page, Manager Type can be used to define the Manager ID or Manager’s Position number of the department. Since Xyz Company has departments centrally organized, thus, this feature will not be used.
The
department/verticals in Xyx Company are listed in the table below.
SNO
Line of Business
Department Code
Department Description
1 XXXX0 100 Actuary
2 XXXX0 120 Admn
3 XXXX0 140 Claims
4 XXXX0 160 Corporate
1 XXXX0 100 Actuary
2 XXXX0 120 Admn
3 XXXX0 140 Claims
4 XXXX0 160 Corporate
Job Code:
Job code is an identification of job description Xyz
Company maintains Designations and Salary grades for an employee. The
designation can be mapped to PeopleSoft Job Code. Job Code has standard hours,
work period, compensation frequency etc.
Navigation: Set Up HRMS> Foundation Tables>Job Attributes> Job Code Table
Compensation:
Compensation is a systematic approach to providing monetary value to
employees in exchange for work performed. Compensation may achieve several
purposes assisting in recruitment, job performance, and job satisfaction.
Ex
- Base
Pay
- Commissions
- Overtime
Pay
Salary Plan:
Salary Plans define salary components and default values for the components
Salary Plans define salary components and default values for the components
Navigation: Set Up HRMS > Product Related> Compensation> Base Compensation >Salary Plan
Salary Grade:
Every company
will maintain their own salary grades Xyz Company hires employees in one of the following grades:
Navigation: Set Up HRMS> Product Related> Compensation> Base Compensation> Salary Grade
Pay group:
A pay group is a logical grouping of employees based on
shared characteristics that facilitate payroll processing because of common
requirements such as employee type, pay frequency, same country location, and
so on. A pay group consolidates a set of employees within a company for payroll
processing.
Navigation: Main
Menu > Set Up HCM > Product Related > Payroll For North America >
Payroll Processing Controls > Pay group Table .
Create Shift Table:
It provides an overview of shifts and discusses how to set up a
shift.
If your organization doesn't use
multiple shifts, you must still set up the Not Applicable (N/A) shift with
blank values in the Shift table for each pay group set ID. N/A is the default
shift in Job data. Setting up this shift avoids potential processing errors if
an earnings code is created with Elig for Shift Differential selected (the
default value).
Navigation =>Set Up HCM >
Related > Payroll for North
America > Compensation and Earnings > Shift Table.
Table Set Control:
Table Set controls
associate business units with record groups and set IDs. Each business unit has
its own Table Set control, which is stored on the Table
Set Record Group Control table. You can associate a set ID for each individual
record group to a business unit.
Table Sets are groups of control tables that
enable you to share the same control values among multiple business units. This
reduces data redundancy by enabling multiple business units to access shared
information while keeping information such as departments decentralized. You
can use business units and Table Sets to associate a business unit with
individuals in the enterprise or to specify default values for a business
unit's transactions.
Navigation : People Tools> Utilities> Administration>
Table Set Control.
Here we need to change the Record Group Id (PY_O2,HR_01,HR_02,HR_03) set id as your created Set id.





































Excellent Inthiyaz Tapal..
ReplyDelete